|

Lesson 9.3 Hypothesis Test for a Population
Mean – Unknown Population Standard Deviation
Hypothesis Testing for a
Population Mean When the Population Standard
Deviation is Unknown
When the population standard deviation is
unknown, the distribution for a hypothesis test of
a single population mean is the Student-t
(explained in this lesson).
The statistic is the sample mean calculated from
the data. We use it together with the degrees of
freedom to calculate the p-value.
The underlying population has a normal
distribution.
Hypothesis Testing Problems
Using TI-83 or TI-84 calculators
Example: A television chef claims that commercial
Italian salad dressing has, on average, at most
6.5 grams of fat in it. He randomly selects six
different brands of Italian salad dressing at a
supermarket. The grams of fat per serving are 7,
7, 9, 6, 8, 5. Assume the underlying population is
normal and conduct an appropriate hypothesis test.
The important numbers are the:
- claim that the population
mean is at most 6.5 grams
- data
Formulate the 2 hypotheses.
The first sentence, a television chef claims that
commercial Italian salad dressing has, on average,
at most 6.5 grams of fat in it." tells us the null
hypothesis. The "at most" translates as a "less
than or equal to" symbol and goes into Ho.
Since the hypotheses are contradictory, the
alternate hypothesis must have a ">" in it. The
test is right-tailed.
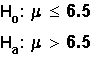
Determine the random variable and the
distribution for the test.
Student-t because the population standard
deviation is unknown.
Using the statistic calculated from the data,
calculate the p-value.
Enter the data into list L1 and
use TI-83 or TI-84 calculator functions STAT
TESTS 2:T-Test. The calculator automatically
calculates the sample mean and the degrees of
freedom from the data.
-
Inpt: Data
-
μo: 6.5
-
List: L1
-
μ: > μo
-
Calculate
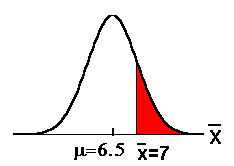
The p-value (p) is 0.2130 to 4
decimal places.
Compare α and the p-value and make
a decision.
Assume α = 0.05 since none is
given.
Since 0.05 < 0.2130 (α< p-value), we
do not reject Ho.
Write an appropriate conclusion.
We conclude that the there is at
most 6.5 grams of fat, on average, in commercial
salad dressing.
Example
Most workers are interested in the
length of an average work week. The following
hypothesis testing problem uses data to
determine if a work week for a startup company,
on average, is 65 hours or less than 65
hours. Close the window when you are
finished viewing the example. You will return
here.
Think About It
Do the Try-It examples in Introductory
Statistics. Verify the numbers using your
calculator. The calculator instructions follow the
problem.
Please continue to the next section
of this lesson.
Up » 9.1
Hypothesis Testing
» 9.2 Hypothesis Testing -
Known » 9.3 Hypothesis Testing-
Unknown »
9.4 Hypothesis Testing for a Single Population
Proportion » 9.5 Type I and II Errors
|